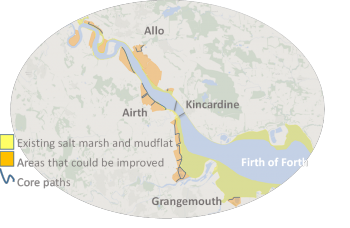
Operationalising ecosystem services in the Sudoeste Alentejano e Costa Vicentina Natural Park, Portugal
Submitted by Anonymous on 16 January 2017Supporting the design of policies and planning instruments to ensure the sustainable management of natural capital stocks and the delivery of critical ecosystem services in the Natural Park. Engaging local stakeholders and decision makers throughout the process to promote awareness raising and social learning.