URBES Berlin - A thriving city embraces its green spaces
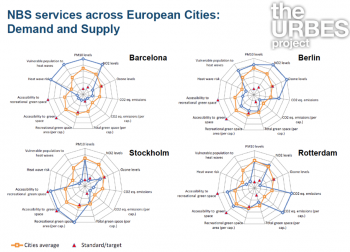
Submitted by Frederic Lemaitre on 14 May 2018The URBES project focusses on functional diversity, urban ecosystem services and NbS, institutions, economics and resilience science and worked to translate research insights into principles, landscape designs and applications. It explores the drivers behind loss/enhancement of urban ecosystem services delivered by nature based solutions such as urban green space, monetary and non-monetary valuation of biodiversity and ecosystem services in the urban landscape and what are the most effective mechanisms for the governance of non-marketed ecosystem services.
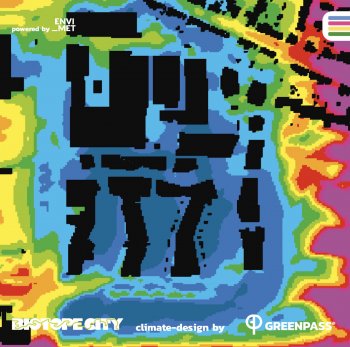
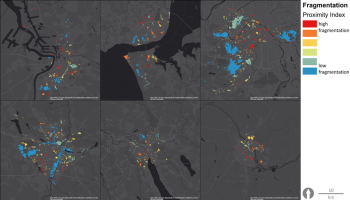
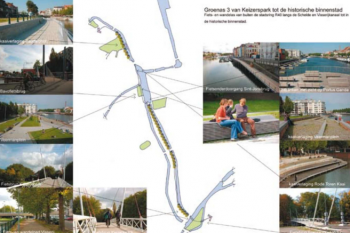
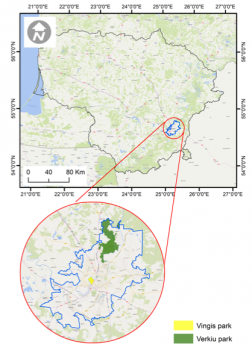
In the Berlin case study,...